AWS open source newsletter #156
May 8th, 2023 - Instalment #156
Welcome
Hello and welcome to the AWS open source newsletter, #156, the newsletter that just keeps on giving….in this case, keeps giving you brand new open source projects to practice your four freedoms on. So what do we have for you this week? Coming up later in this newsletter we have projects such as “sustainability-scanner” helps you check your Cloudformation templates against sustainability good practices, “synthtable” helps you create synthetic data for different use cases, “neptune-gremlin-client” a Java based Gremlin client, “s3zipper” a tool to quickly download entire S3 buckets, “chataws” a nice demo of how you can use ChatGPT to aid your AWS deployments, and plenty of other great projects.
We also have great content covering some of your favourite open source technologies, and this week we have OpenSearch, Amazon Corretto, Apache Kafka, Apache Airflow, Suricata, Grafana, GraphQL, PostgreSQL, Amazon EMR, Kubernetes, Amazon EKS, Spring Cloud AWS, MySQL, PyTorch, MLFlow, Redis, Apache Spark, Zarr, AWS Amplify, AWS CDK, DuckDB, and other topics featured.
Feedback
Please please please take 1 minute to complete this short survey and bask in the warmth of having helped improve how we support open source.
Celebrating open source contributors
The articles and projects shared in this newsletter are only possible thanks to the many contributors in open source. I would like to shout out and thank those folks who really do power open source and enable us all to learn and build on top of what they have created.
So thank you to the following open source heroes: Aidan Steele, AJ Stuyvenberg, Banjo Obayomi, Gabriel Soltz, Steve Roberts, Brad Webber, Ben Kehoe, Wenqi Glantz, Maximilian Schellhorn, Ciro Greco, Kevin Purdy, Danny Steenman, Bhuvanesh, Petar Forai, Michael Meidlinger, João Pedro, Aashish Nair, Parnab Basak, Danny Banks, Tricia Jamison, Greg Sommerville, Maciej Walkowiak, James McIntyre, Ali Alemi, Rajkishan Gunasekaran, Krishna Sarabu, and Nathan Taber.
Latest open source projects
The great thing about open source projects is that you can review the source code. If you like the look of these projects, make sure you that take a look at the code, and if it is useful to you, get in touch with the maintainer to provide feedback, suggestions or even submit a contribution.
Tools
s3zipper
s3zipper is another nice tool from AWS Hero Aidan Steele, that provides a couple of Lambda functions that let you use S3 Object Lambda Access Points to download ZIP files of directories in S3 on-demand. Once deployed, you don’t need any special tools installed on your client - anything that can download from S3 will do.
lambda-stream
lambda-stream from AWS Community Builder AJ Stuyvenberg has put together this project that implements AWS Lambda Response Streaming in TypeScript. The library adds types and local support for AWS Lambda response streaming. It drops in to any framework (Serverless, CDK, SAM, SST) and acts as an adapter for tests.
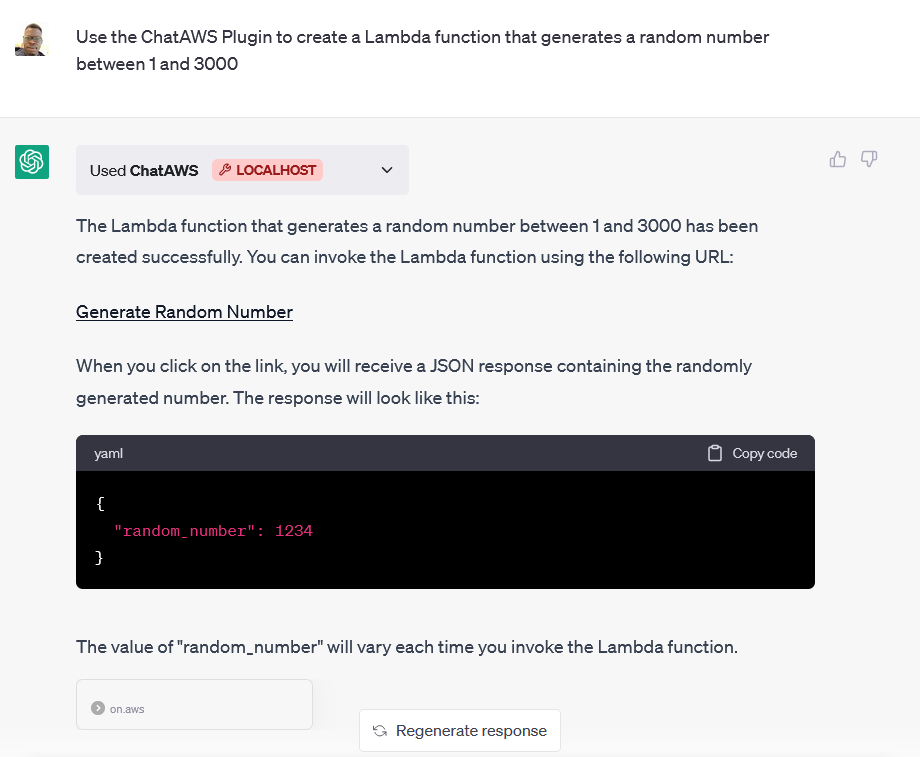
chataws chataws is a project from my colleague Banjo Obayomi that is a ChatGPT plugin simplifying AWS deployments. Banjo has helpfully provided a blog post to help you get started, so make sure you read ChatAWS: Deploy AWS Resources Seamlessly With ChatGPT. Check out the repo for a demo of this in action.
aws-arn aws-arn is a project from Gabriel Soltz that provides a complete* list of all AWS ARNs. (* Gabriel points out that not all services are covered yet, but is work in progress)
sustainability-scanner
sustainability-scanner is an open source tool that helps you create a more sustainable infrastructure on AWS. It takes in your Cloudformation template as input, evaluates it against a set of sustainability best practices and generates a report with a sustainability score and suggested improvements to apply to your template. SusScanner comes with a set of rule implementations aligned to the AWS Well-Architected Pillar for Sustainability. However, this is not an exhaustive list and new rules will come out as the tool evolves.

synthtable
synthtable is sadly not a homage to 80s synth music, rather it is a useful guided CLI wizard that generates synthetic tabular data without requiring any ML knowledge or coding. Built using open-source package SDV, it creates high-quality, realistic data sets for testing, development, and research. It has a user-friendly interface with guided prompts makes it easy for users to generate the exact data they need, all while ensuring privacy and security.
neptune-gremlin-client
neptune-gremlin-client is a Java Gremlin client for Amazon Neptune that allows you to change the endpoints used by the client as it is running. Includes an endpoint refresh agent that can get cluster topology details, and update the client on a periodic basis. You can supply your own custom endpoint selectors to configure the client for a subset of instances in your cluster based on tags, instance types, instance IDs, Availability Zones, etc. The client also provides support for connecting to Neptune via a proxy such as a network or application load balancer, as an alternative to using an endpoint refresh agent and custom endpoint selectors.

Demos, Samples, Solutions and Workshops
aws-batch-celery-worker-example
aws-batch-celery-worker-example is an example project for running compute intensive Celery workers using AWS Batch. To show you how you can deploy this project, you can read the follow along blog post, Run Celery workers for compute-intensive tasks with AWS Batch.

bobs-used-bookstore-sample
bobs-used-bookstore-sample is a sample application built on ASP.NET Core 6.0 that aims to represent a simple, real-world application. It is a monolithic n-tier application with an ASP.NET Core MVC front end and a Microsoft SQL Server database backend. To help you get started there are a couple of blog posts you can read. First up is, Introducing Bob’s Used Books—a New, Real-World, .NET Sample Application, where Steve Roberts provides an overview of this sample project, and then we have Introducing Bob’s Used Books: A .NET Sample Application (Part 1), where Brad Webber describes how to get up and running with Bob’s Used Books as quickly as possible, and explore the different debug and deployment modes that are available. Watch out for future posts that dive deeper into this project.
kms_random
kms_random this short Gist from AWS Hero Ben Kehoe provides a simple proof of concept of using AWS KMS as a randomness generator in your Python code. As Ben points out in this accompanying documentation - “I do not vouch for the randomness properties of the results. Presumably using the same logic as SystemRandom should work, but I am not an expert in cryptography or randomness.”
Karpenter
Check out the new Karpenter workshop. Karpenter is an open-source project that provides an efficient and scalable way to manage Kubernetes cluster autoscaling. In this workshop you will dive deep into the concepts of Karpenter with hands-on labs and examples. As part of the exercises, you will also learn how using Karpenter can improve application availability, lower compute cost and minimise operational overhead.
Advanced EKS Immersion Workshop, Karpenter
AWS and Community blog posts
Community roundup
There were so many great community authored posts last week, it was tough to choose between them. These are the ones that caught my eye. As regular readers might know, I have a soft spot for all things Java, so Wenqi Glantz’s post Going Serverless With Spring Cloud Function, AWS Lambda Java 17 Support, and SnapStart really hit the spot. The post looks at how to develop and deploy a Java Lambda function, built on Spring Cloud Function using the recently added Java 17 support (that is based on Amazon Corretto). Keep with the Java theme, airhacks.fm podcast featured Maximilian Schellhorn who talks about lots of things including creating Java content on AWS, SnapStart, AWS Serverless Java containers, and more. From Java to DuckDB, an open-source in-process SQL OLAP database built specifically for analytical queries. Ciro Greco has put together A Serverless Query Engine from Spare Parts that shows you how to build a simple end-to-end application in AWS on a serverless infrastructure. Be sure to check that one out. Two core Unix-like utilities, sudo and su, are getting rewrites in Rust from Kevin Purdy looks at some work we are doing at AWS to collaborate with some open source projects that many use and depend upon, and develop Rust based versions of those tools. Danny Steenman shares how to you can organise your AWS CDK projects in his post, Optimize your AWS CDK Project Structure for Growth and to close this community round up, we had Bhuvanesh who shared some benchmarks he has been doing in his post, AWS Graviton 3 vs Graviton 2 — A SysBench on RDS MySQL - be sure to read the post to see what he found.
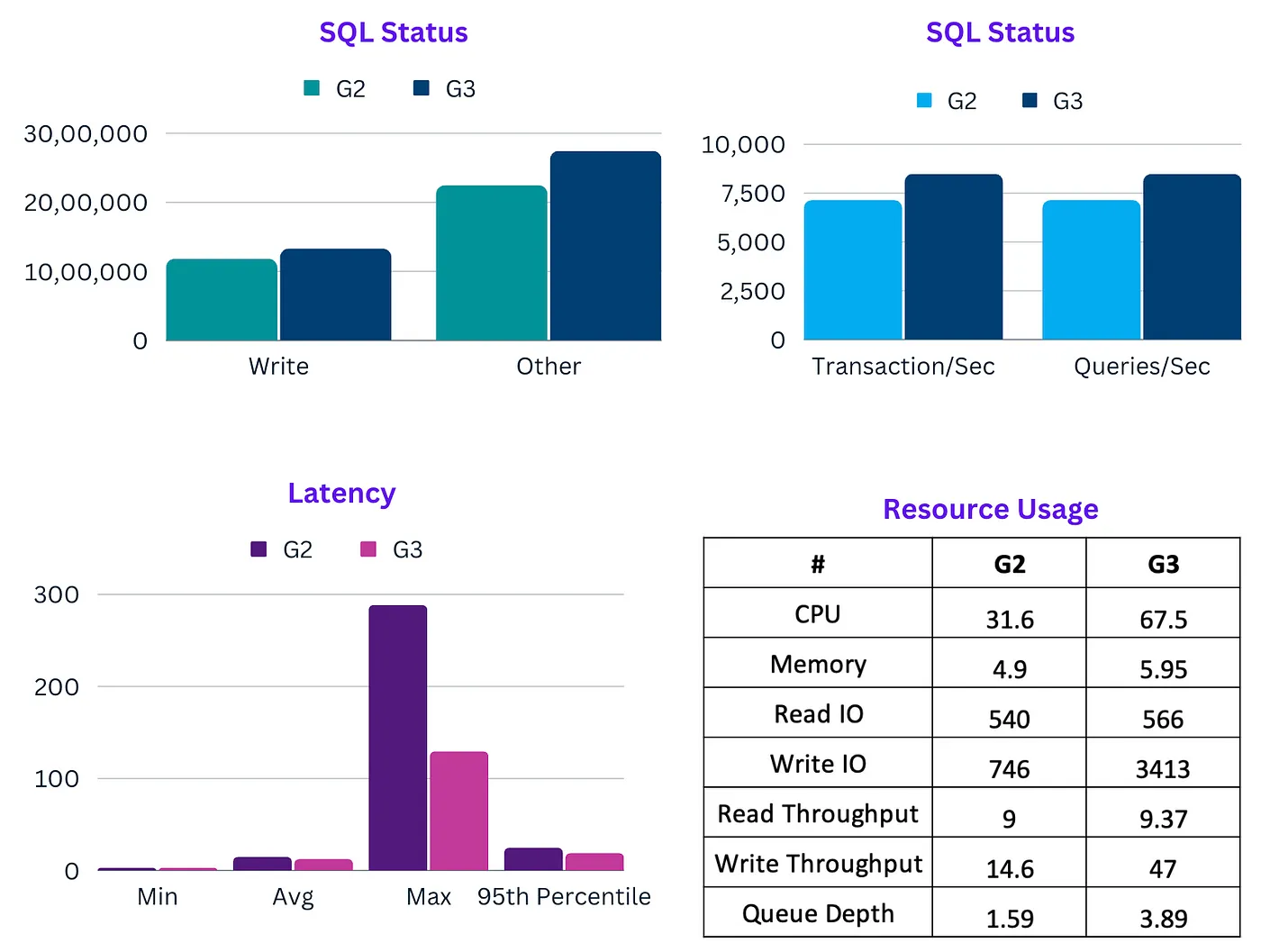
Apache Airflow
Traditionally, batch processing has been a domain of the Linux operating systems, but what if you needed to modernise your Windows Server batch processing workloads? In the post, Batch processing for Microsoft Windows Server workloads on AWS Petar Forai and Michael Meidlinger show you a reusable and general framework for running Windows Server batch processing workloads on AWS, which leverages Amazon Managed Workflows for Apache Airflow (Amazon MWAA) to orchestrate those batch jobs. Very nice post.

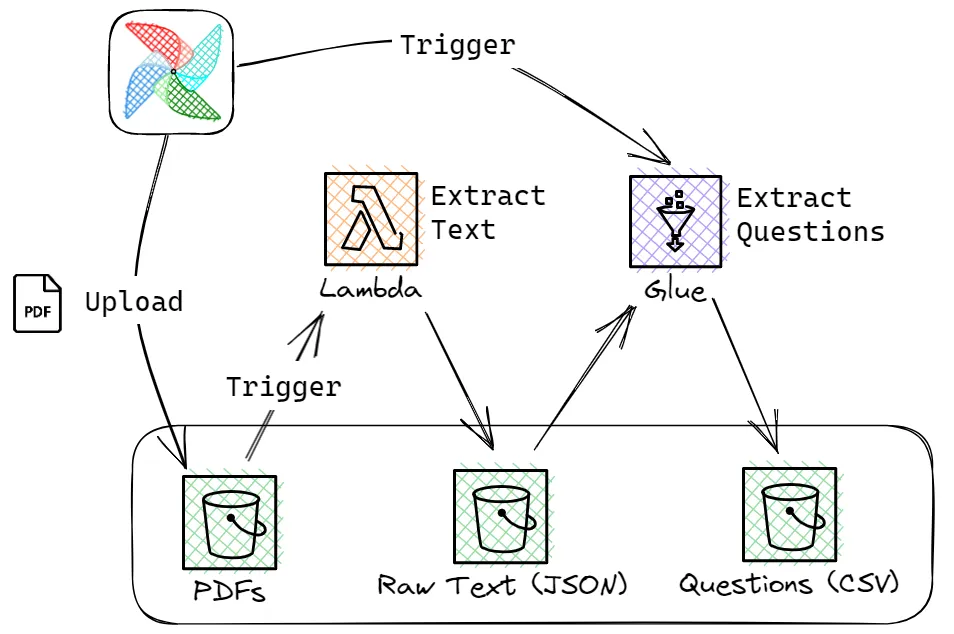
From the AWS Community there were a couple of posts I want to share. I really enjoyed reading João Pedro’s journey in creating data pipelines with Apache Airflow in his post, Data Pipeline with Airflow and AWS Tools (S3, Lambda & Glue). João provides a detail walkthrough (and supporting code) to show you how he build a nice solution to automate the extraction of questions from actual exams papers that are available as PDFs on the MEC (Ministry of Education) website.
Following that was the post from Aashish Nair, Creating a YouTube Data Pipeline with AWS and Apache Airflow, who shares how he used Apache Airflow to build a pipeline to answer two questions: What are the most popular [You Tube] video categories in each country?, and Does the most popular video category change over time? If so, how? Aashish provides links to the code so you can try this yourself.
Finally, last week Parnab Basak provided a nice post, What’s new with Amazon MWAA support for Apache Airflow version 2.4.3 that looked at some of the great new features available with Apache Airflow 2.4.3 that you can now deploy in Amazon MWAA support for Apache Airflow (MWAA).

AWS Amplify
In the post, Announcing the Amplify UI StorageManager Component, Danny Banks shows you a new cloud-connected UI component called the StorageManager, which lets your users upload and manage files to the cloud. [hands on]

Zarr
Zarr is a Python package providing an implementation of compressed, chunked, N-dimensional arrays, designed for use in parallel computing. Unlike legacy file formats, the cloud-native Zarr format is designed for virtual and efficient access to compressed chunks of data saved in a central location such as Amazon S3. In the post, Decrease geospatial query latency from minutes to seconds using Zarr on Amazon S3 Tricia Jamison and Greg Sommerville walk you through a hands on example of converting Network Common Data Form (NetCDF, a format commonly used to store geospatial data such as climate and weather) datasets to Zarr, and show the performance benefits of using cloud-native data formats such as Zarr with object storage such as Amazon S3 increase as well. [hands on]

Check out the repo, convert-netcdf-to-zarr
Other posts and quick reads
- [Cloud Native] Start Pods faster by prefetching images is a nice, hands on guide that proposes a design to speed up container start up times, that allows you to pre-pull images on nodes without managing infrastructure or Kubernetes resources [hands on]

- [AI/ML] Optimized PyTorch 2.0 inference with AWS Graviton processors looks at the potential cost savings for PyTorch inference with AWS Graviton3-based Amazon Elastic Cloud Compute C7g instances across Torch Hub Resnet50, and multiple Hugging Face models relative to comparable EC2 instances
- [AI/ML] Track machine learning experiments using InfinStor MLflow with Amazon SageMaker Studio shows you how to use InfinStor MLflow with Amazon SageMaker Studio to experiment, collaborate, train, and run inferences using this ML platform [hands on]
- [Big Data] How SOCAR handles large IoT data with Amazon MSK and Amazon ElastiCache for Redis is a follow on post that looks at how SOCAR built a streaming data pipeline to process IoT data for real-time analytics and control, providing a detailed overview of streaming messages with Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (Amazon MSK) and Amazon ElastiCache for Redis [hands on]
- [Big Data] Monitor and optimize cost on AWS Glue for Apache Spark demonstrates a tactical approach to help you manage and reduce cost through monitoring and optimization techniques on top of your AWS Glue workloads [hands on]
- [Database] Deploy schema changes in an Amazon Aurora MySQL database with minimal downtime walks you through performing schema changes with minimal downtime on production workloads [hands on]

Quick updates
Spring Cloud AWS
Maciej Walkowiak tweeted news about version 3.0 of Spring Cloud AWS. According to Maciej:
it’s pretty much a complete rewrite of the project on AWS SDK v2.
And some of the key things to know is that it is compatible with Spring Boot 3.0 and enables developers to perform simple testing with localstack. Grab the full details over at the release notes
OpenSearch
OpenSearch 2.7.0 is ready for download! The latest version of OpenSearch offers a range of new capabilities for search, analytics, observability, and security applications, along with significant enhancements to administration and usability. Read more in the post from James McIntyre, Get Started with OpenSearch 2.7.0
Apache Kafka
Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (Amazon MSK) now supports Apache Kafka version 3.4.0 for new and existing clusters. Apache Kafka 3.4.0 includes several bug fixes and new features that improve performance. Key features include a fix to improve stability to fetch from the closest replica. Amazon MSK will continue to use and manage Zookeeper for quorum management in this release.
In addition to this was news that Amazon MSK now offers multi-VPC private connectivity that simplifies connectivity and access to your Amazon MSK clusters from your Apache Kafka clients hosted in any VPC or AWS account. We are launching multi-VPC private connectivity (powered by AWS PrivateLink) that allows you to easily establish cross-VPC and cross-account connectivity between your Apache Kafka clients and your Amazon MSK cluster, while keeping all traffic within the AWS Network. With a few clicks, you can turn on multi-VPC private connectivity for one or more authentication modes on your cluster. This feature is supported for IAM, SASL SCRAM, and mutual TLS authentication modes. You can then create Amazon MSK managed VPC Connections and use them to allow your Apache Kafka clients to connect privately to the cluster. You can also now provide access for Apache Kafka clients to connect privately from a different AWS account through a cluster policy. By combining with this with MSK’s IAM functionality, you can also provide these clients fine grained access control to Apache Kafka resources on the cluster. Together, IAM based authentication and cluster policies simplify permission management for cross-account connectivity to an MSK cluster. Multi-VPC private connectivity is available with pay-as-you-go pricing and is supported in all AWS regions where MSK is available.
Read the post, Connect Kafka client applications securely to your Amazon MSK cluster from different VPCs and AWS accounts, where Ali Alemi looks at this new capability in more detail.

Amazon EMR
Amazon EMR on EKS enables customers to run open-source big data frameworks such as Apache Spark on Amazon EKS without having to manage application provisioning themselves. This week we had a couple of updates.
First up we had news that Amazon EMR on EKS now supports vertical autoscaling, a feature to automatically tune the memory and CPU resources of EMR Spark Applications to adapt to the needs of the provided workload, offering a simplified mechanism for customers to tune resources, enhance reliability and optimise costs. EMR Spark allows users to configure the amount of Memory and CPU cores that it will utilise. However, tuning these values has until now been a manual process for customers that can be complex. For instance, too little memory can result in out-of-memory exceptions but allocating too much can result in over-spending on idle resources. Vertical autoscaling automatically scales the memory and CPU allocated to an EMR Spark application based on its real-time and historic resource utilisation. This simplifies the process of tuning resources and optimising costs for an application while helping improve its reliability.
Dive deeper by checking out this post, Improve reliability and reduce costs of your Apache Spark workloads with vertical autoscaling on Amazon EMR on EKS, where Rajkishan Gunasekaran shows you how you can use vertical autoscaling to easily monitor resource utilisation for one or more EMR on EKS jobs without any impact to your production workloads.

We also saw that you can now self-hosted Jupyter notebooks as another mechanism to run interactive workloads via managed endpoints. Amazon EMR on EKS customers setup and use a managed endpoint (available in preview) to run interactive workloads using an integrated development environments (IDEs) such as EMR Studio. Customers currently rely on EMR Studio to run Jupyter notebooks for their interactive Spark workloads, which provides a managed notebooks solution without having to worry about customising the execution environment where they run. With self-hosted Jupyter notebooks, customers that require such customisation now have a choice of where they control the notebook execution environment, with the flexibility to decide where it runs and the ability to change how to access it, helping them meet their specific business needs. The self-hosted Jupyter notebooks feature is supported on Amazon EMR on EKS 6.10 release and later.
PostgreSQL
Two important new updates this week.
First up is news that Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) for PostgreSQL now supports the pgvector extension to store embeddings from machine learning (ML) models in your database and to perform efficient similarity searches. Embeddings are numerical representations (vectors) created from generative AI that capture the semantic meaning of text input into a large language model (LLM). pgvector can store and search embeddings from Amazon Bedrock, Amazon SageMaker, and more. By using pgvector on Amazon RDS, you can simply set up, operate, and scale databases for your ML-enabled applications. The pgvector extension allows you to build ML capabilities into your e-commerce, media, health applications, and more to find similar items within a catalog. For example, a streaming service can use pgvector to provide a list of film recommendations similar to the one you just watched. The pgvector extension is available on all database instances in Amazon RDS running PostgreSQL 15.2 and higher.
Find out more by reading the post, Building AI-powered search in PostgreSQL using Amazon SageMaker and pgvector where Krishna Sarabu provides a hands on guide to building a product catalog similarity search solution by integrating Amazon SageMaker and Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) for PostgreSQL with the pgvector extension.

Following that is news that Amazon Aurora Serverless v1 now supports PostgreSQL major version 13. PostgreSQL 13 includes improved functionality and performance from enhancements such as de-duplication of B-tree index entries, improved performance for queries that use partitioned tables, incremental sorting to accelerate data sorts, parallel processing of indexes with the VACUUM command, more ways to monitor activity within a PostgreSQL database, new security capabilities, and more. Aurora Serverless v1 also supports in-place upgrade from PostgreSQL 11 to 13. Instead of backing up and restoring the database to the new version, you can upgrade with just a few clicks in the AWS Management Console or using the latest AWS SDK or CLI. No new cluster is created in the process which means you keep the same endpoints and other characteristics of the cluster. The upgrade completes in minutes and can be applied immediately or during the maintenance window. Your database cluster will be unavailable during the upgrade.
GraphQL
AWS AppSync is a fully managed service that enables developers to build scalable, performant APIs that connect applications to data and events. Today, we announce the general availability of Private API support for AWS AppSync. With Private APIs, you can now create GraphQL APIs that can only be accessed from your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (“VPC”). With AppSync Private APIs, you need to only configure your API as “private” and AppSync will automatically limit access to your API’s GraphQL and realtime subscription endpoints to interface VPC Endpoints in a shared AWS account. Traffic to a Private API uses connections that are designed to be secure and does not leave the Amazon network.
Suricata
AWS Network Firewall now allows you to override the Suricata HOME_NET variable making it easy to use AWS managed rule groups in firewalls that are deployed in a centralized deployment model. Managed rule groups are collections of predefined, ready-to-use rules that AWS writes and maintains for you. The Suricata HOME_NET variable of the managed rule group has the Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) range which is inspected by the AWS Network Firewall. Previously, you were unable to override HOME_NET variable as it used the CIDR ranges of VPC where the firewall is deployed. If your firewall uses a central inspection VPC, AWS Network Firewall populates HOME_NET with CIDR ranges of the inspection VPC, instead of the application (spoke) VPCs which you want to filter.
Starting today, you can override the HOME_NET variable in firewall policy to include the CIDR ranges of all the VPCs that you want to inspect. This allows you to protect your application VPCs using managed rule groups in centralised firewall deployment. There is no additional charge to use this feature. You can override the Suricata HOME_NET variable in firewall policy using the Amazon VPC Console, AWS CLI, or the Network Firewall API.
Grafana
Amazon Managed Grafana is a fully managed service for Grafana, a popular open-source analytics platform that enables you to query, visualise, and alert on your metrics, logs, and traces. Since inception, Amazon Managed Grafana maintained a single version offering across all workspaces globally. With this release, you can select an Amazon Managed Grafana supported version to create a new workspace. Version 9.4 includes several new features to further enhance your experience in Amazon Managed Grafana including, but not limited to: plugin enhancements to support CloudWatch cross-account querying, OpenSearch serverless, querying multiple asset properties from AWS IoT Sitewise, query result reuse and async queries for Athena; Prometheus and Loki query builders make it even easier to create and modify queries for your data sources; Service accounts that provide a secure and efficient way to automate tasks within your Grafana instance.
If you want to find out more, read on in “Announcing Amazon Managed Grafana workspace version selection with version 9.4 support”
Videos of the week
KubeCon
Check out Nathan Taber’s keynote at KubeCon for a really nice summary of some of the work going on to support open source projects and communities.
Build on Open Source
For those unfamiliar with this show, Build on Open Source is where we go over this newsletter and then invite special guests to dive deep into their open source project. Expect plenty of code, demos and hopefully laughs. We have put together a playlist so that you can easily access all (eight) of the episodes of the Build on Open Source show. Build on Open Source playlist
Events for your diary
If you are planning any events in 2023, either virtual, in person, or hybrid, get in touch as I would love to share details of your event with readers.
Reducing the costs of your openCypher applications Online, May 8th, 4pm UK
openCypher is an open-source project for creating graph applications. Neptune supports openCypher graph query language, and in this webinar you will learn more about the cost benefits for moving openCypher workloads to Neptune serverless. With Neptune serverless, customers can see up to 90% cost savings compared to provisioning for peak capacity. A demo of Neptune in action will be included in this session.
Head over to the You Tube holding page, Reducing the costs of your openCypher applications
Intelligent Document Processing with AWS and Open Source with Hugging Face AWS Office Zurich, May 23rd 8am - 2pm CET
For readers who are based in Zurich, make sure you check out this event. The goal of this in-person event is to learn and share experience on how to get insights from documents, and simplify workflows using document processing and the power of open source. There is a great line up of speakers and an excellent agenda.
Find out more and reserve your space by heading over to, Intelligent Document Processing with AWS and Open Source with Hugging Face
Open source Table Formats with AWS Glue and Amazon EMR Online, 6th June 5PM UK time
Curious about Transactional Data Lakes? Come join our AWS experts as we take you through the most popular open source table formats, how these table formats can help you enable a modern data strategy, and how to build on these formats with Amazon EMR and AWS Glue. In this session, we’ll cover some of the key differences between these different table formats, help you decide which table format may be the best fit for your workloads, and show you how to start building today.
You can join via YouTube live here
Cortex Every other Thursday, next one 16th February
The Cortex community call happens every two weeks on Thursday, alternating at 1200 UTC and 1700 UTC. You can check out the GitHub project for more details, go to the Community Meetings section. The community calls keep a rolling doc of previous meetings, so you can catch up on the previous discussions. Check the Cortex Community Meetings Notes for more info.
OpenSearch Every other Tuesday, 3pm GMT
This regular meet-up is for anyone interested in OpenSearch & Open Distro. All skill levels are welcome and they cover and welcome talks on topics including: search, logging, log analytics, and data visualisation.
Sign up to the next session, OpenSearch Community Meeting
Stay in touch with open source at AWS
Remember to check out the Open Source homepage to keep up to date with all our activity in open source by following us on @AWSOpen
